New Economy Movement (NEM) is an enterprise-wide solution designed to fuel the blockchain-based economic revolution. Originally designed to be a fork of NXT, the community decided to adopt a completely new source code with an alpha version released on June 25th, 2014 and the first stable version on March 31st, 2015.
NEM is not just a cryptocurrency, but an ecosystem born in 2015, which has also generated and fuels a cryptocurrency called XEM.
The project is based on 3 entities:
- The NEM Foundation
- The NEM Blockchain (on which NEM services such as Smart Assets are based)
- XEM, which is the cryptocurrency
The NEM Smart Asset system
The NEM blockchain adopts what they call the “Smart Asset System”. An intelligent open-source system and customisable by anyone as it offers powerful integrations using the APIs provided by the software.
The NEM Smart Asset system allows the customisation of the use of the blockchain with a series of services aimed at simplifying the use of things such as domain-like namespaces and Multi-signature controls.
The blockchain is protected and transactions are processed by a global network of nodes running the NEM core software, this network is then used as a gateway API server.
This means that developers who want to create blockchain-based apps do not have to run any particular or dedicated NEM software as all functionality is available simply by logging in with the API.
This allows great flexibility in terms of system design and app usage within the network. Apps that directly access the NEM API have a dedicated server or can use existing servers that are adapted to use NEM in the background.
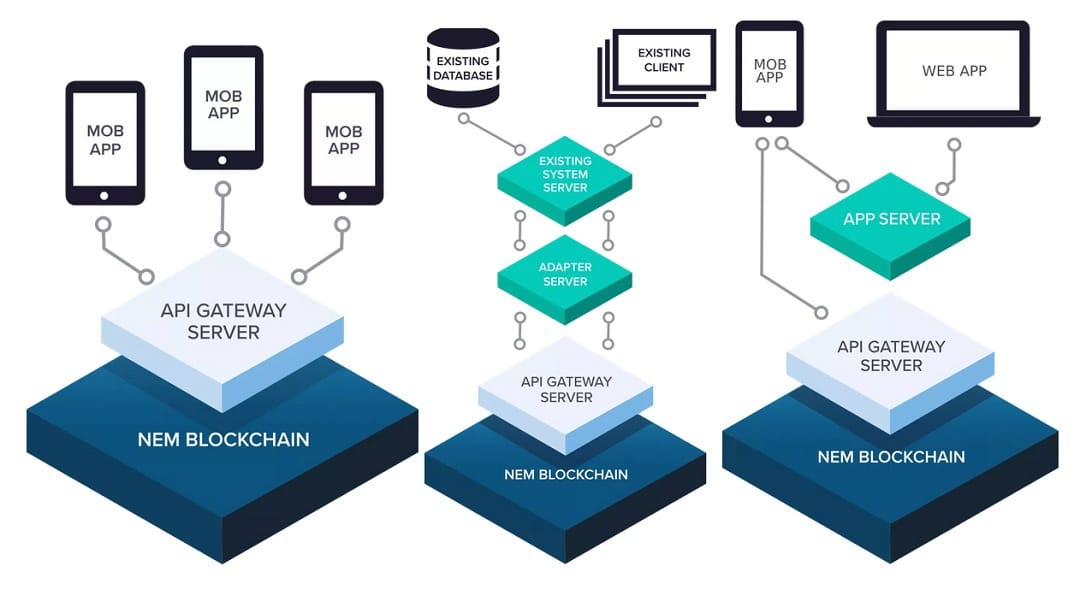
Developers specify NEM addresses that act as asset containers, these addresses can be updated and changed over time. An address could simply represent a wallet containing tokens or something more complex such as a document requiring signatures.
These developers then create so-called Mosaics: transferable assets that represent coins and signatures and that will reside within the addresses. This system of flexible addresses and configurable mosaics can be used for countless use cases.
Proof-of-Importance and Harvesting
NEM’s Blockchain relies on an algorithm known as Proof-of-Importance (which differs from the more well-known Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake) to reach consensus through a process that encourages active participation in the network. This makes it a decentralised network and rich in well-structured nodes.
Each node has an “importance score” that determines the frequency with which it can “collect” XEM, the native token of NEM.
The “Proof of Importance” is activated by a process similar to that followed by the Proof-of-Stake, but adds a number of variables such as network clustering and most importantly new ranking criteria.
An algorithm has been developed for the Proof-of-Importance that is used in NEM transactions that allows determining the importance of a certain user based on the amount of XEM present in the account and according to the number of transactions they make with their wallet. The importance of a NEM user transaction is determined both by the amount of currency and by the number and quality of transactions carried out. The PoI uses a ranking system called NCDawareRank that allows to measure and monitor all the indicators that determine a consensus. The PoI works in such a way as to evaluate NEM transactions mainly on the basis of criteria such as volume and confidence of each transaction.
The initial tokens of Nem
Part of this system works with the coins initially residing in the wallet: when they are stored in this way they are initially “unvested coins” that is, simple tokens.
Over time, those coins will start to “get vested” and to matter more, making the account important. In order to benefit from this “importance score”, the account must have at least 10000 matured XEM.
The NEM transaction chart is constantly being analysed to provide information on which nodes are contributing and which are not. This means that the more transactions are sent to other users and thereby the more the network is used, the greater the importance that will be attributed to them.
The number of transactions and the importance that is given to the nodes generate scores that are then used to adjust the probability of the node collecting XEM.
Since the PoI does not require intensive hardware, nodes can work at full capacity on almost all machines regardless of power. This is a major advantage of NEM, which prevents the centralisation of the system.
In some systems such as Bitcoin, mining blocks and the use of a network node are two separate processes. In the NEM system, however, these are executed by the same software.
Other features of this blockchain
NEM uses a customised version of the EigenTrust ++ algorithm which implements a system whereby each node tracks the information it receives from other nodes (new blocks, transactions, etc.) and then checks this information.
If the information proves to be valid, the “reputation” of the node will increase and, if the information is incorrect, the “reputation” will decrease. The reputations of all nodes are then passed over the network and updated within each node. This allows automatic load balancing and removal of damaged nodes from the network, keeping it as smooth and fast as possible.
Additional features:
- Built-in spam filters prevent unnecessary transactions from flooding the network and clogging it;
- A P2P time synchronisation system that allows the network to maintain accurate timestamps without relying on external servers to control time;
- An encrypted messaging system based on blockchain; more information on this technology can be found on the NEM technology web page while technical details can be found in the technical reference section.
Public vs Private
Anyone can use the public NEM blockchain using the API. However, for applications that require more privacy, it is possible to “provision” a private version of the NEM blockchain on proprietary internal servers and use only nodes chosen by the user.
On this network of private and “reliable” nodes, the control features mentioned above can be removed, allowing even faster transactions in a sort of “closed box” configuration.
The ease of development, flexibility and unique PoI system make NEM a very attractive platform for any developer or company looking to build their own blockchain-based system.
Currently, the XEM cryptocurrency is in the 23rd position in terms of market capitalisation (data: CoinMarketCap) and one XEM is worth about 0.055 USD.



