According to a new research by Security Research Labs, all Ethereum clients that have not yet applied the latest patch related to the known vulnerabilities represent an important risk for the security of the entire network.
The report is based directly on data from ethernodes.org and shows how a large number of nodes using the Parity and Geth clients, the most popular ones around, are still vulnerable to malicious attacks.
The main reason is due to the clients’ lack of update despite the fact that the last patch was released at least two weeks ago.
Ethereum security risks: the situation with Parity clients
SRLabs recalls having already reported a vulnerability in the Ethereum Parity client in February that allowed node opening and remote shutdown.
It can be read in the report:
“According to our collected data, only two-thirds of nodes have been patched so far. Shortly after we reported this vulnerability, Parity released a security alert, urging participants to update their nodes”.
A second patch was released on March 2nd, but has not yet been installed by at least 30% of Parity nodes.
An astounding 7% of nodes would still have a version prior to last July, which was the date when an important patch was released to fix a vulnerability in the consensus system.
According to the report, Parity clients should update automatically with each new release but this is not always the case and some updates are lost or underestimated.
Geth clients are not safe at all
The scenario for Ethereum’s Geth clients, unfortunately, seems even worse.
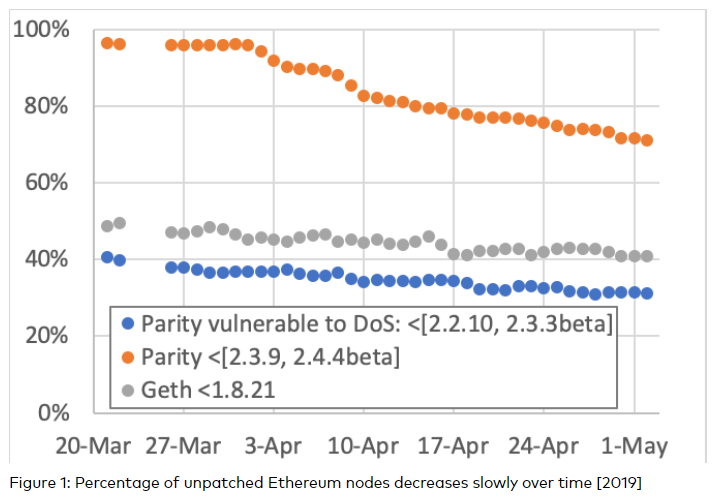
About 44% of Geth nodes visible on ethernodes.org have a lower software version than v.1.8.20, which is the version in which a security-critical update was released.
In addition, Geth, according to the Security Research Labs team, has no automatic update functionality.
A risk for the entire Ethereum network
The number of Ethereum clients exposed would, therefore, be significant and this makes the entire network vulnerable.
The researchers are quite clear in the report:
“If a hacker can crash a large number of nodes, controlling 51% of the network becomes easier. Hence, software crashes are a serious security concern for blockchain nodes (unlike in other pieces of software where the hacker does not usually benefit from a crash)”.



